選択した画像 ultimate yield strength formula 124188-What is yield and ultimate strength
Ultimate Moment Capacity for Symmetrical Flexural Sections for LFD of Bridges calculator uses Maximum Ultimate Moment=yield strength of steel*Plastic Section Modulus to calculate the Maximum Ultimate Moment, The Ultimate Moment Capacity for Symmetrical Flexural Sections for LFD of Bridges formula is defined as maximum factored moment used for design of membersA is the cross sectional area the force is acting onDennis R Moss, Michael Basic, in Pressure Vessel Design Manual (Fourth Edition), 13 Maximum Shear Stress Theory This theory asserts that yielding occurs when the largest difference of shear stress equals the shear yield strengthAccording to this theory, yielding will start at a point when the maximum shear stress at that point reaches onehalf of the uniaxial yield strength, F y
Stress Vs Strain Curve Video Khan Academy
What is yield and ultimate strength
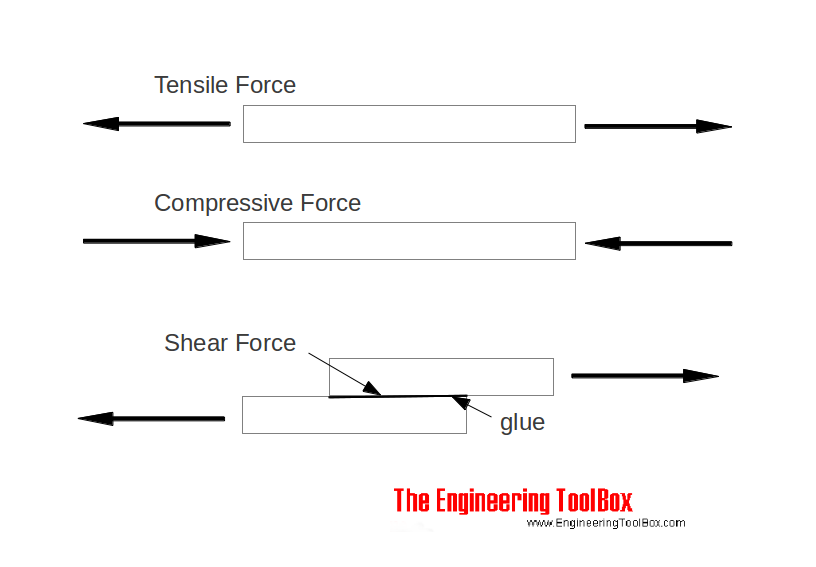
What is yield and ultimate strength-Tensional Strength – Pulling apart Compression Strength – Pushing together Shear Strength – Slicing across Each of these criteria have a 'yield' value and an 'ultimate' value, determined by the shape of the Stress – Strain curve for the materialConvert ultimate tensile to ultimate shear!


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
Should the yield strength (σ γ) be equal to the ultimate tensile strength (UTS), any plastic deformation of the pipe could result in rupture However, with a difference between σ γ and UTS, the ability for the steel to exhibit strain hardening provides some protection for the pipe against fracture, for example, during layingConvert ideal to actual endurance limit!UF is the ultimate force;
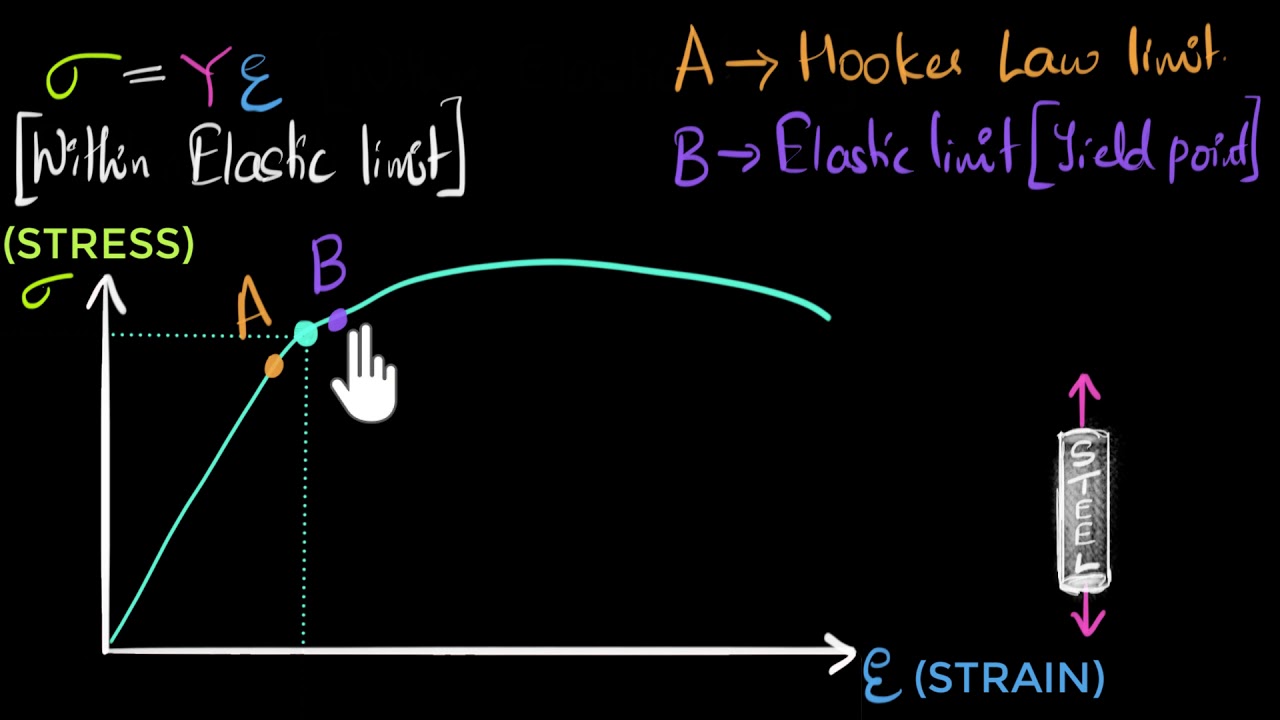
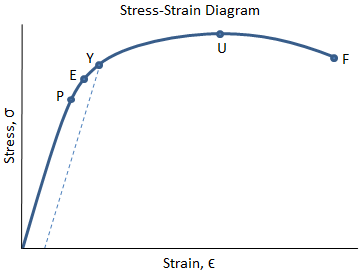
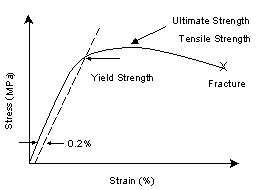
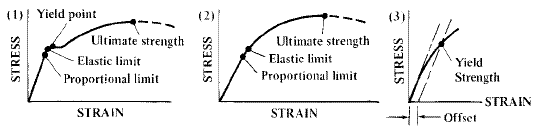
Additionally, the shear strength of the base metal must also be considered φ Rn = 09 x 06 Fy x area of base metal subjected to shear where, Fy is the yield strength of the base metal For example T Elevation Plan T Elevation Plan Strength of weld in shear Strength of base metal = 075 x 0707 x a x Lw x fw = 09 x 06 x Fy x t x LwThe point U indicates the maximum stress that can be achieved by the material It corresponds to its ultimate or tensile strength The point F is the fracture point Note that the points E and Y may coincide for some types of materials such as ferrous materialsTensile strength can also be determined using this formula σ f = P f /A o Where P f is the load at fracture, A o is the original crosssectional area, and σ f is the tensile strength, measured in N/m² or pascals It is important to note that the tensile strength of a material is a specific value under controlled standard test conditions
Ultimate tensile strength is often shortened to "tensile strength" or even to "the ultimate" "Ultimate strength" is sometimes used but can be misleading and, therefore, is not used in some disciplines A number of terms have been defined for the purpose of identifying the stress at which plastic deformation begins The value most commonly usedUltimate Stress Formula The ultimate stress is defined as the maximum tensile stress that a material can withstand before rupture or break when a load is applied It is also referred to as Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) or ultimate strength It is equivalent to the maximum load that can be carried by one square inch of crosssectional areaInstitute International, and uses ultimate strength design Materials f' c = concrete compressive design strength at 28 days (units of psi when used in equations) Deformed reinforcing bars come in grades 40, 60 & 75 (for 40 ksi, 60 ksi and 75 ksi yield strengths) Sizes are given as # of 1/8" up to #8 bars



Estimating Tensile Strength From Yield Or 0 2 Proof Values Twi


Q Tbn And9gcq Lokv6u6biweu7e6sd5mb7neolnaw Dcdbogfctf 8hvcdutp Usqp Cau
Ultimate tensile strength is often shortened to "tensile strength" or even to "the ultimate" If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals)The ultimate tensile strength formula is S = F / A where S = the breaking strength (stress) F = the force that caused the failure A = the least cross sectional area of the material The ultimate tensile stress (UTS) is typically found in a more precise manner by performing a tensile test and recording the engineering stress versus strain curveAxial strength is the product of the crosssectional area (based on nominal dimensions) and the yield strength Combined stress effects All the pipestrength equations previously given are based on a uniaxial stress state (ie, a state in which only one of the three principal stresses is nonzero)


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness
Unit Conversion Calculator & Converter for Tensile/Yield & Charpy values Use the following calculator to convert yield or tensile values in ksi, Mpa, N/mm² or psi Type the value in the box next to Mpa (using the drop down to change the unit of measurement)The stressstrain diagram for a steel rod is shown and can be described by the equation ε=0(1e06)σ0(1e12)σ 3 where s in kPa Determine the yield strength assuming a 05% offsetWhile the ultimate tensile strength of a material is higher than the yield strength, it is a condition that hopefully your fasteners will never see as it represents catastrophic failure or the equivalent of ripping off the arm wrestlers arm Figure 1 shows the relationship of yield strength to ultimate tensile strength


Stress Strain And Young S Modulus



Strength At Break Tensile
( ) ( ) 0917(09)(059)(160τ a τ = 1 Stress amplitude and midrange stress!Determine the yield strength and tensile strength of load dividing the yield load & ultimate load by cross sectional area of the bar Gauge length = 8 inch Determine the yield strength by the following methods Offset Method To determine the yield strength by the this method, it is necessary to secure data (autographic or numerical) from



Stressing Structure



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress
The known failure point of a material (ie, ultimate yield strength or tensile strength subject to a safety factor of 09 or more) In ASCE/SEI 710, the design wind speeds are higher than in previous editions The change is to provide for "Ultimate Wind Speeds" and isUTS) is (almost) the point at which necking initiates, ie plastic instability sets in That means the geometric softening dominates the workBrittle materials do not exhibit any yield point So they do not have yield strength


Tensile Stress Formula For 21 Printable And Downloadable Fust



Solved 3 10 Pts Suppose We Are Given The Following Dat Chegg Com
There may be situations where yield or proof strength values of steel are known, but ultimate tensile strength (UTS) values have not been reported As the knowledge of UTS is important for quantifying strainhardening properties, an estimation scheme has been developed under the European project SINTAP 1Tensile Strength Formula The following formula is used to calculate a tensile strength TS = UF / A Where TS is the tensile strength;Spect to fatigue strength, hardness, and tensile and yield strength MacGregor's twoload was used for determination of the true stressstrain curve for alloy 625 at room temperature The twoload test requires no strain measurement during the test, and only the maximum and fracture loads are recorded Data for



Characteristic Strength Of Materials Characteristic Load Or Ultimate Load



Tensile Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Yield strength The stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation This is not a sharply defined point Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate strength The maximum stress a material can withstandYield Strength Take the minimum yield in psi of the ASTM grade (see our Strength Requirements by Grade Chart for this value), multiplied by the stress area of the specific diameter (see our Thread Pitch Chart) This formula will give you the ultimate yield strength of that size and grade of boltThe point Y is the yield point which corresponds to the yield strength of the material;


What Is The Difference Between Tensile And Yield Strength Quora
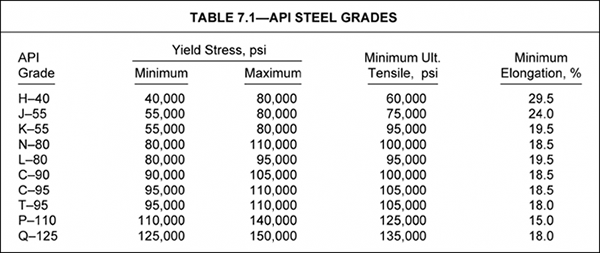


Tesile Property Of Pipe Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations
Tensile Yield Strength Unit Conversion Calculator;Yield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress (usually represented in PSI) that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing or breakingThe point at which a material ceases to be elastic and becomes permanently plastic, the point at which it yields, is called its yield point The magnitude of stress at which this transition occurs is known as the material's yield stress or strength The yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behavior


What Is 0 2 Of Offset Method In Yield Strength Quora
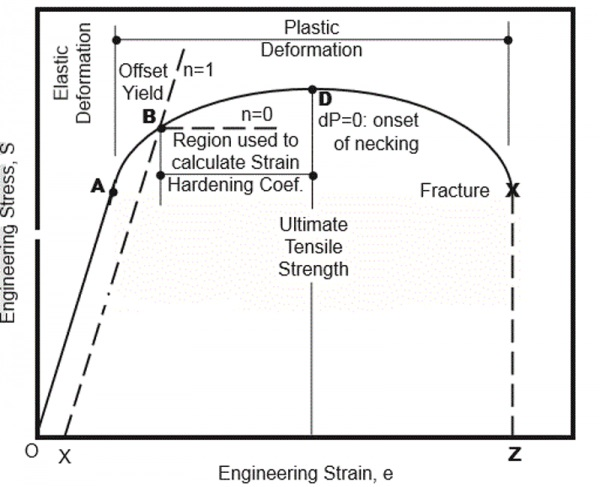


Which Methods To Use For Sheet Metal Tension Testing
While the ultimate tensile strength of a material is higher than the yield strength, it is a condition that hopefully your fasteners will never see as it represents catastrophic failure or the equivalent of ripping off the arm wrestlers arm Figure 1 shows the relationship of yield strength to ultimate tensile strengthApproximate ideal endurance limit!S!e =05S ut =05(3)=160MPa S S us n m es Safety factor based on Goodman criterion!Ultimate tensile strength is often shortened to "tensile strength" or even to "the ultimate" If this stress is applied and maintained, fracture will result Often, this value is significantly more than the yield stress (as much as 50 to 60 percent more than the yield for some types of metals)



Failure Theories Static Loads



Ultimate Tensile Strength Uts Stress Strain Curve
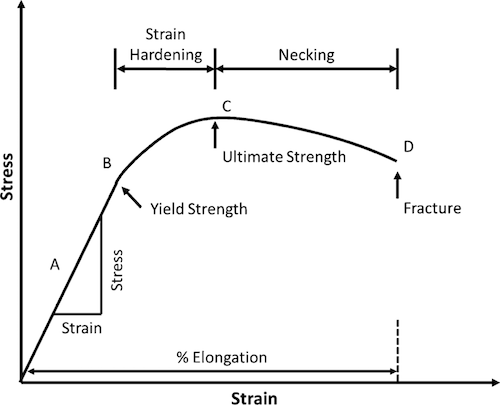
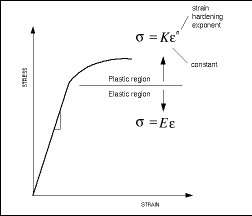
Fracture strength is the value corresponding to the stress at which total failure occurs Stiffness is how a component resists elastic deformation when a load is applied Hardness is resistance to localized surface deformation The strength of a material can refer to yield strength, ultimate strength, or fracture strengthLimit, yield strength have been used for the first property For the failure stress such terms as ultimate strength, strength, rupture, and limiting stress and many more have been used All of these have had rather different interpretations None have been entirely satisfactory and none universally adoptedRambergOsgood Equation The stressstrain curve is approximated using the RambergOsgood equation, which calculates the total strain (elastic and plastic) as a function of stress where σ is the value of stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, S ty is the tensile yield strength of the material, and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which can be calculated based on



Ultimate Tensile Strength Importance Testing Examples Fractory
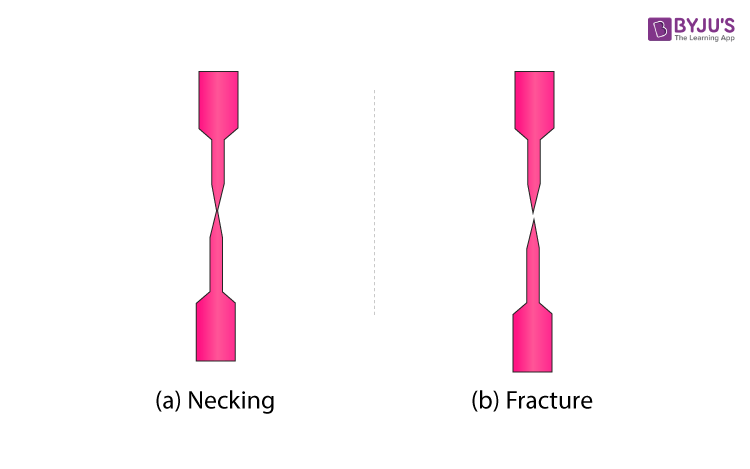


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
Additionally, the shear strength of the base metal must also be considered φ Rn = 09 x 06 Fy x area of base metal subjected to shear where, Fy is the yield strength of the base metal For example T Elevation Plan T Elevation Plan Strength of weld in shear Strength of base metal = 075 x 0707 x a x Lw x fw = 09 x 06 x Fy x t x LwShould the yield strength (σ γ) be equal to the ultimate tensile strength (UTS), any plastic deformation of the pipe could result in rupture However, with a difference between σ γ and UTS, the ability for the steel to exhibit strain hardening provides some protection for the pipe against fracture, for example, during layingThe point U indicates the maximum stress that can be achieved by the material It corresponds to its ultimate or tensile strength The point F is the fracture point Note that the points E and Y may coincide for some types of materials such as ferrous materials


Http Www Csun Edu Bavarian Courses Mse 527 Tension Test Mse 527l Pdf
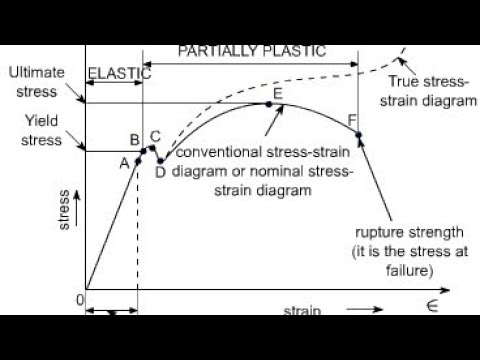


Stress Vs Strain Curve Yield Point Yield Strength Elastic Limit Neking Ultimate Tensile Youtube
Determine the yield strength and tensile strength of load dividing the yield load & ultimate load by cross sectional area of the bar Gauge length = 8 inch Determine the yield strength by the following methods Offset Method To determine the yield strength by the this method, it is necessary to secure data (autographic or numerical) from"Calculation of the increase in yield strength due to the effects of cold work of forming By Ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, mechanical behaviour ViewThe yield calculation will determine the safety factor until the part starts to plastically deform The ultimate calculation will determine the safety factor until failure On brittle materials these values are often so close as to be indistinguishable, so is it usually acceptable to only calculate the ultimate safety factor



Ultimate Tensile Strength Importance Testing Examples Fractory
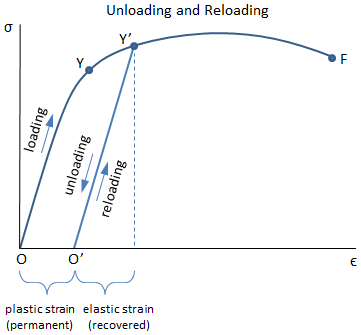


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
"Calculation of the increase in yield strength due to the effects of cold work of forming By Ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, mechanical behaviour ViewUltimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimateWhen yield strength is reported, the amount of offset used in the determination should be stated For example, "Yield Strength (at 02% offset) = 51,0 psi" Young's Modulus of Common Engineering Materials



Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The minimum yield strength is the key property of steel used in pipeline design See Figure 1110This figure shows the relationship between stress and strain The minimum yield strength is defined as the tensile stress required to produce a total elongation of 05%(k c converts tensile endurance to shear endurance!)!The tensile strength is measured by the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking Ultimate strength can be defined for liquids as well as solids under certain conditions Below given the ultimate tensile strength formula to calculate the ultimate strength of any material



How To Find Yield Strength Quora



Solved A Ductile Material Has A Yield Strength Of Sy 150 Chegg Com
The tensile strength (or ultimate tensile strength;Yield Strength The yield strength or yield point of the material is defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Ultimate StrengthInstitute International, and uses ultimate strength design Materials f' c = concrete compressive design strength at 28 days (units of psi when used in equations) Deformed reinforcing bars come in grades 40, 60 & 75 (for 40 ksi, 60 ksi and 75 ksi yield strengths) Sizes are given as # of 1/8" up to #8 bars



Ch 2 Stress Strains And Yield Criterion



Mechanical Testing Tensile Testing Part 1 Twi
Yield Strength The yield strength or yield point of the material is defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Ultimate StrengthThe point Y is the yield point which corresponds to the yield strength of the material;
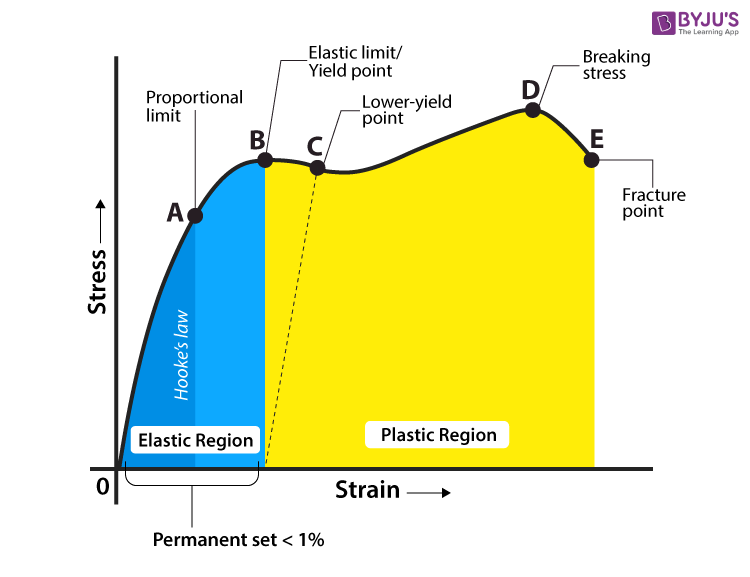


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



What Is The Relationship Between Ultimate Tensile Strength Young Modulus And Elongation At Break


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau


Q Tbn And9gcttwoqta7jtsg 3vilhdf Yhokhwjyvlxmyndyl3ieisjtj3uoc Usqp Cau
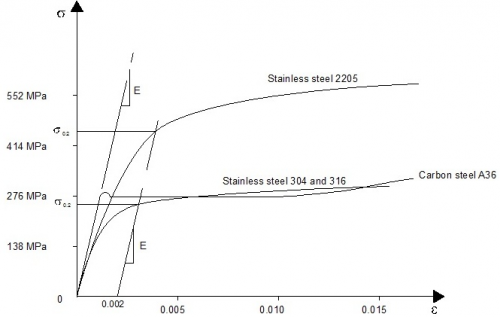


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info
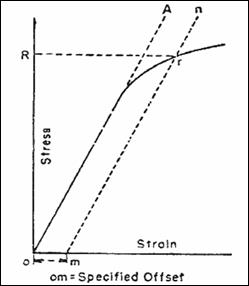


To Determine Yield Strength Tensile Strength Of A Steel Bar By Offset Secant Method


Basic Of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity And Its Calculation Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations



Strength At Break Tensile



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


What Are Tensile Strength Units Quora


Burst Pressure What It Is And Why It S So Important Corrosion Materials



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
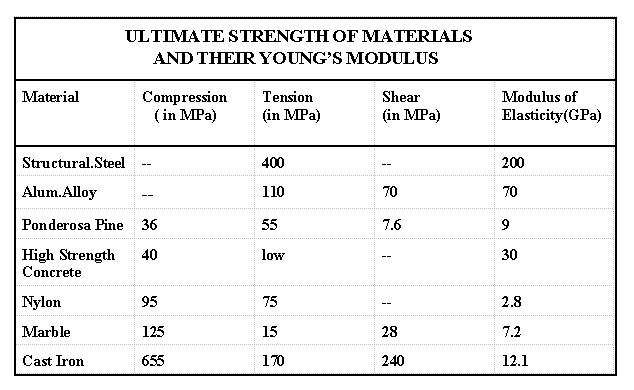


Strength



Need Help With Fundamentals Mechanical Engineering General Discussion Eng Tips



Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations
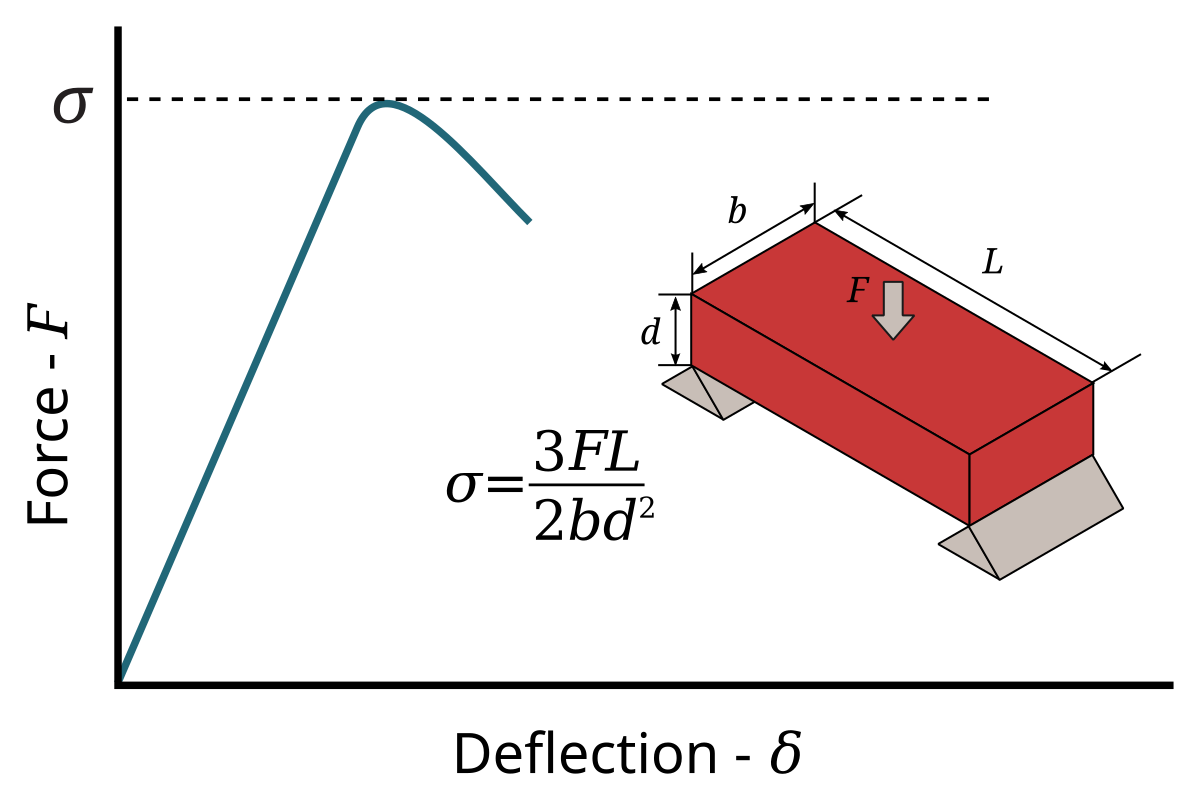


Flexural Strength Wikipedia



Calculation Methods Of Yield Strength And Ultimate Tensile Strength By Download Scientific Diagram



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Calculation Methods Of Yield Strength And Ultimate Tensile Strength By Download Scientific Diagram



Isbt212 04 3 Stress And Strain Proportional Limit And Yield Strength Youtube



Stress Vs Strain Curve Video Khan Academy


Efatigue Glossary Ultimate Strength


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers
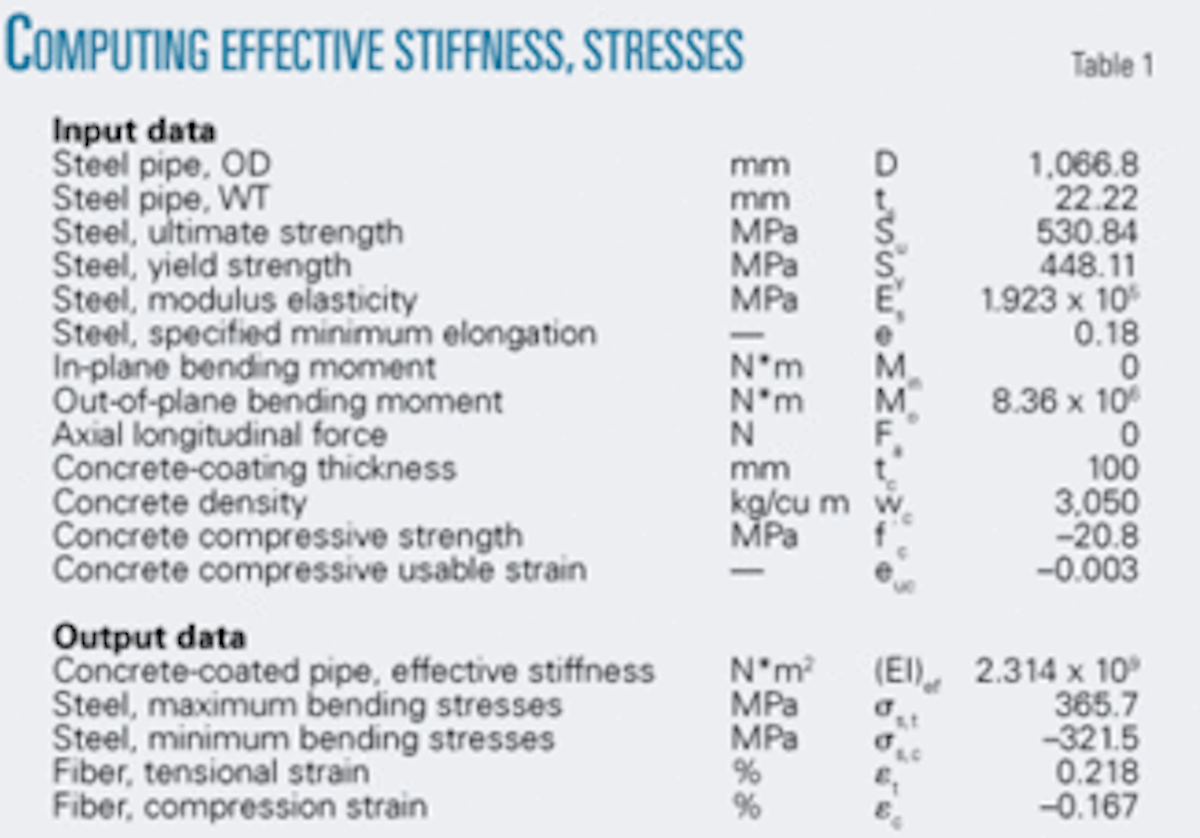


New Method Sets Concrete Coating S Effect On Pipeline Stiffness Stress Oil Gas Journal



Shear Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Influence Of Temperature On Mechanical Properties Fracture Morphology And Strain Hardening Behavior Of A 304 Stainless Steel



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
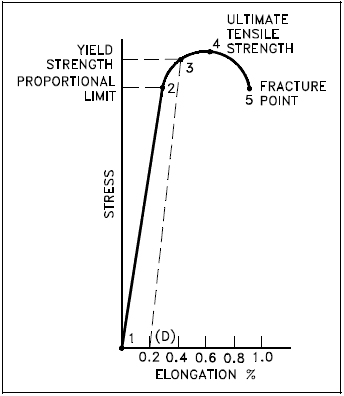


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve



Allowable Stress In Asme Viii 1 3 Api 650 Api 653 Amarine



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel



Strength At Break Tensile



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
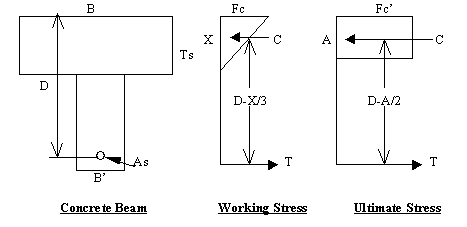


Introduction To Reinforced Concrete Structural Design An Online Course For Engineers And Land Surveyors


Basic Of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity And Its Calculation Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations



Ch 2 Stress Strains And Yield Criterion


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I



Allowable Stress In Asme Viii 1 3 Api 650 Api 653 Amarine
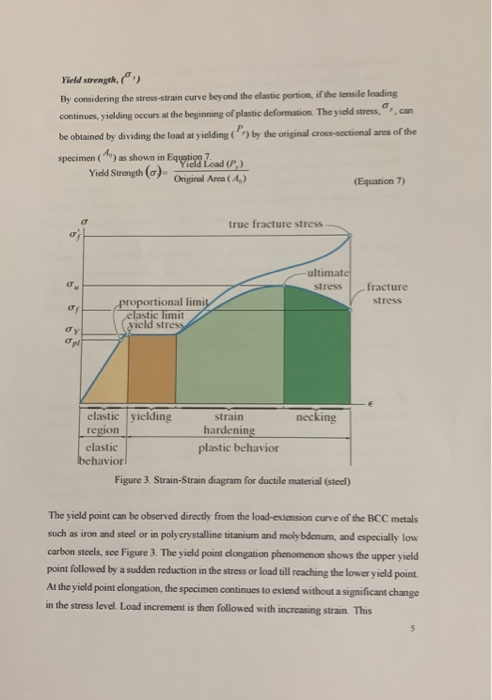


Solved Solve The Results From Page 10 By Using The Rules Chegg Com



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc



Smts And Allowable Stress Amarine


Safety Factor How Do I Calculate That Fea For All
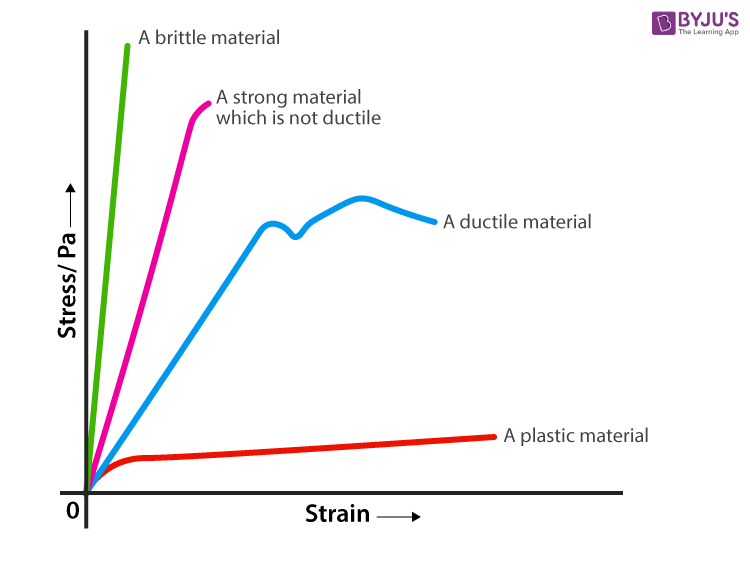


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
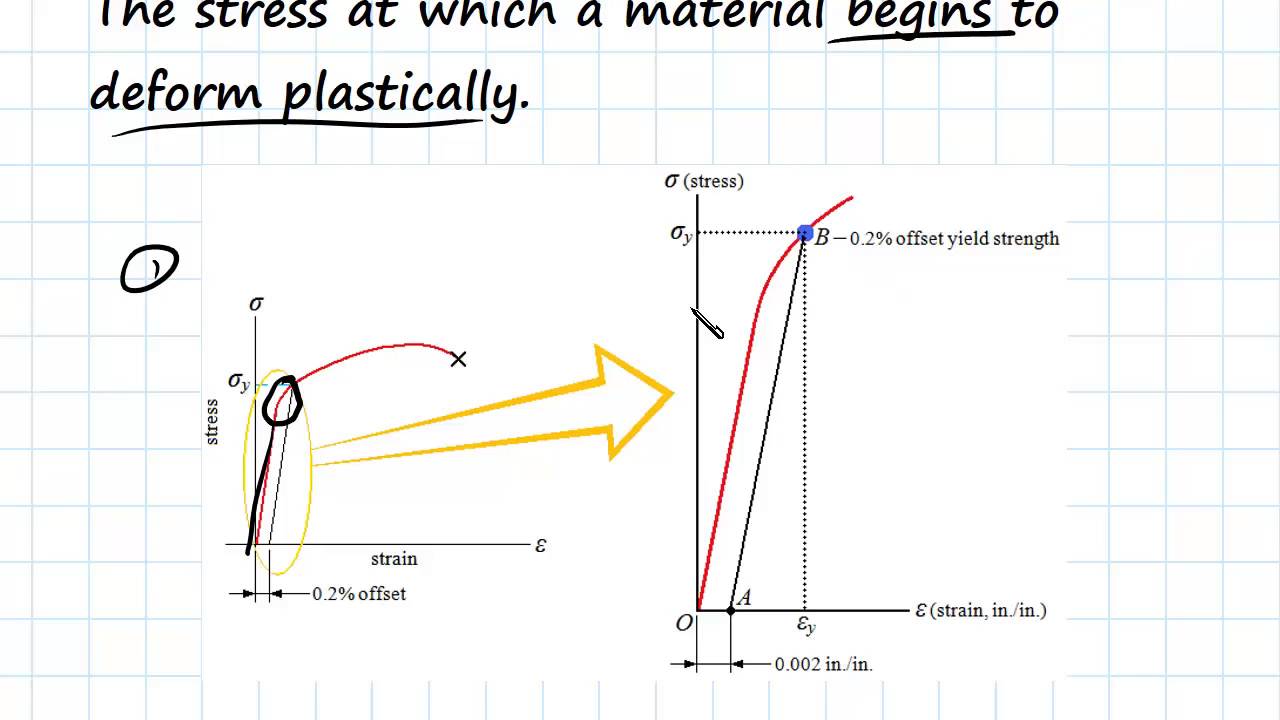


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube


Being Inventive Safety Factor Of Brittle And Ductile Materials



Yield Strength



Calculate Yield Stress Youtube
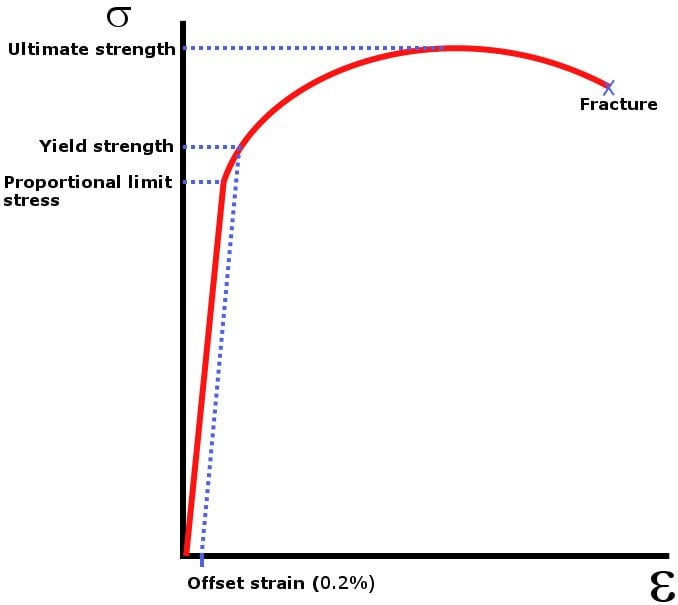


What Is Ultimate Tensile Strength Science Abc



Yield Strength Versus Ultimate Strength Physics Stack Exchange
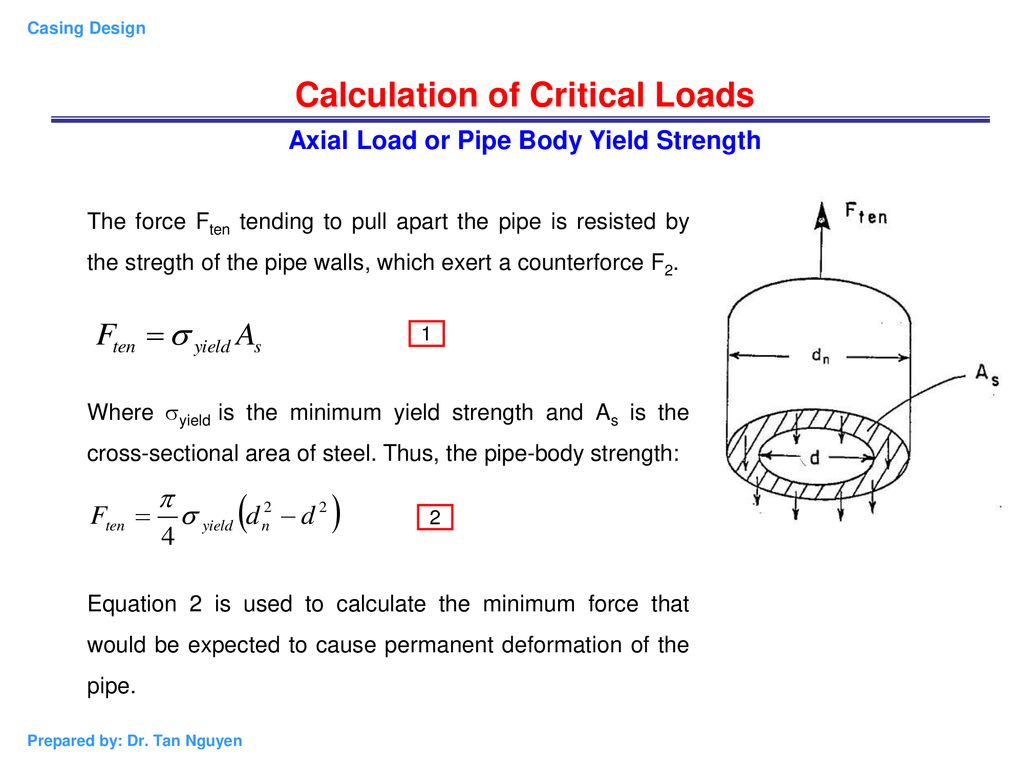


Chapter 2 Casing Design Calculations Of Loads On A Casing Ppt Download
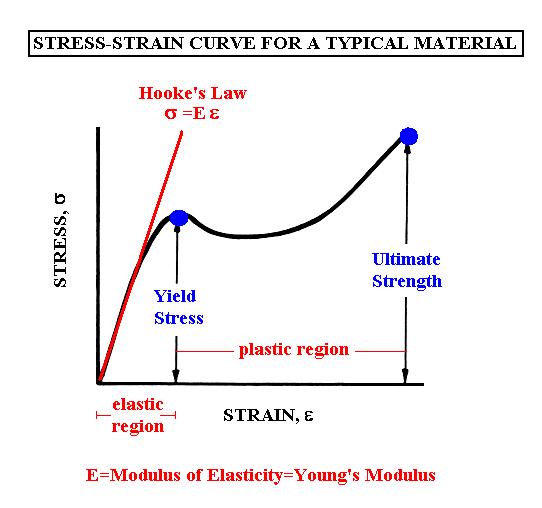


Strength


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
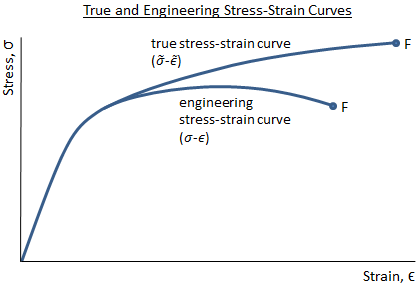


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
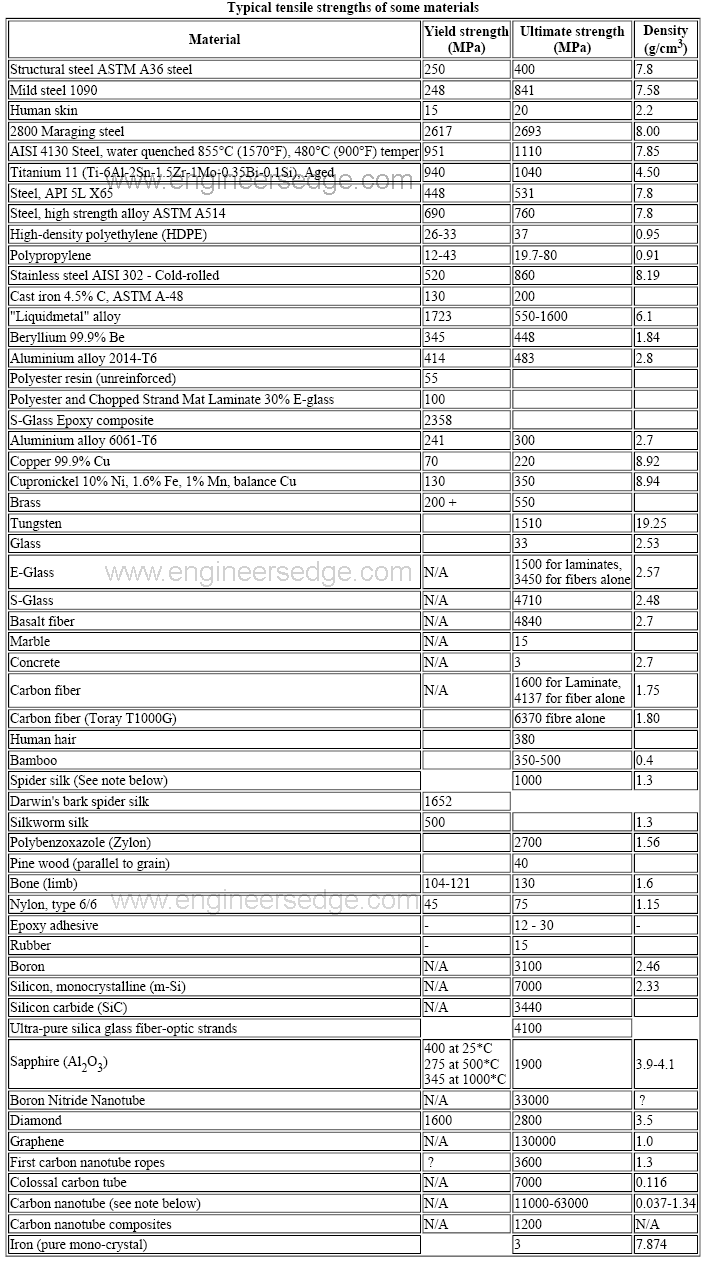


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Why Your Nds Nail Calcs Could Be Wrong And What You Can Do About It Simpson Strong Tie Structural Engineering Blog


Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 Bf Pdf


Engineering Stress Strain Curve
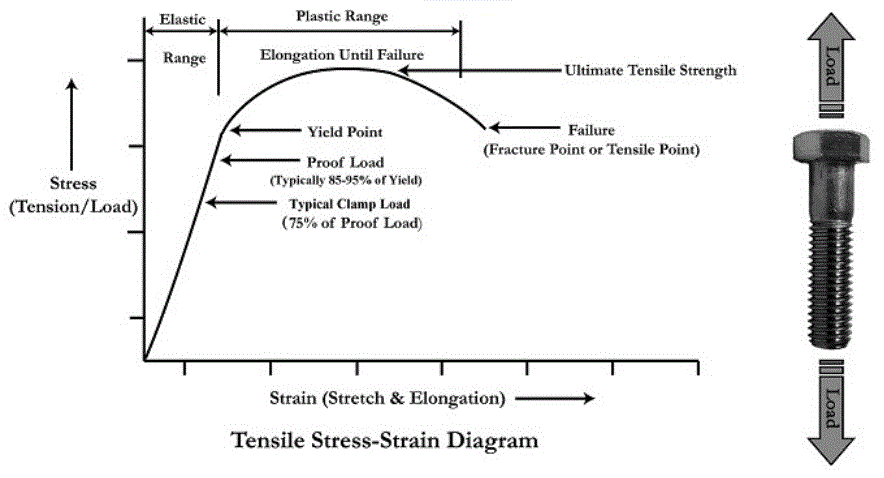


Thread Yield And Tensile Strength Equation And Calculator Engineers Edge Www Engineersedge Com



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



A Yield Strength Rp0 2 And Ultimate Tensile Strength Rm B Download Scientific Diagram



A Comparative Evaluation Of Metallurgical Properties Of Stainless Steel And Tma Archwires With Timolium And Titanium Niobium Archwires An In Vitro Study Vijayalakshmi R D Nagachandran K S Kummi P Jayakumar


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Failure Strength Sf From Re Rm R 0 2 E And Efailure



What Is The Formula For Tensile Strength How Is This Determined Quora



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel



Yield Engineering Wikipedia


コメント
コメントを投稿